Potato
Greasy Cutworm/ Black cut worm
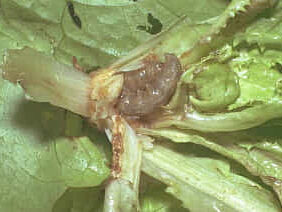
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Eggs: Creamy white, dome-shaped eggs, laid singly on lower surface of the leaves
Larvae: Newly emerged young larva is yellow in colour. The full-grown larva is dark or dark brown with a plump and greasy body.
Pupa: Dark brown pupae are found in earthen cells lying underground in the potato fields
Adult: Dark with some grayish patches on the back and dark streaks on the forewings.





Management
Potato tuber moth
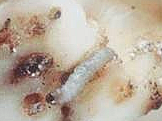
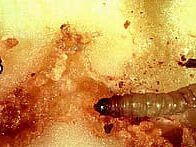
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Egg: Laid singly on the ventral surface of foliage and exposed tubers
Larva: Yellow coloured caterpillar with dark brown head
Pupa: Pupation occurs within a cocoon among the trash, clods of the earth in the field
Adult: Small narrow winged moth, greyish brown forewings and hind wings are dirty white




Management
White grubs
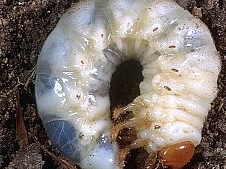
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Larva: “C” shaped grub
Adult: Brown beetle with pale prothorax


Management
Tobacco Caterpillar
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Egg: Masses appear golden brown
Larva: Pale greenish with dark markings
Adult: Forewings are brown in colour with wavy white marking, hind wings are white in colour with a brown patch along the margin



Management
Green Leaf Hopper
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Egg: Elongated yellow-white egg is deposited in leaf vein.
Nymph: Pale-green, wedge shaped, winged pads extend up to the fifth abdominal segment
Adult: It is a wedge shaped and pale green insect


Management
Green peach aphid
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
It resembles wingless adult but the size is small.




Management
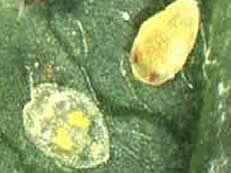
Whitefly
Symptoms of damage
Identification of pest
Egg: Smooth, sub elliptical, stalked at broader basal end with light yellow colour when freshly laid, turn dark brown later on
Nymph: Pale-yellow in colour
Adult: It is small winged insect having light yellow colour. Wings are pure white with prominent long legs.


Management
Source: https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/
