Oil Palm
Spindle bug
Symptoms of damage
Spindle bug - generally noticed in nursery seedlings and field planted young seedlings.
Adults and nymphs of spindle bug live in the innermost two to three leaf axils.
Suck sap from the spindle of leaves
Necrotic lesions which later on turn into dry brown patches.
In severe infestation the spindle fails, to open.
Management
Ploythene sachets - filled with Phorate 10 G (Thimet 10G), @ 2g per sachet, placed in the innermost two leaf axils (one sachet each in a leaf axil).
The same sachets can be used for 6 – 8 months.
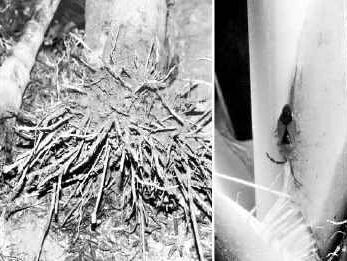
Rhinoceros beetle
Symptoms of damage
Adult beetles bore into the palms and chew the tender tissues
Spindle to break and droop.
Entry holes - presence of chewed-up tissues.
Infested leaves - shortened, broken and distorted.
Fruits - the upper portion of the bunch get underdeveloped and dried.
Damage to the heart of the palm - way for the entry of fungi and bacteria,
Induce rotting in the bud.
Identification of pest
Grub: Sluggish, white, ‘C’ shaped.
Adult: Stout brownish black with a horn projecting from the head.


Management
1. Cultural control
All possible breeding sites are to be eliminated from the plantation.
2. Mechanical
The adult beetles which burrow deep into the crowns of young palm
Extracted by means of a hooked out (metal rod)
After extraction of the beetle, the leaf axils around the injured spindle are to be filled with a mixture of
mancozeb (fungicide) and fine sand at the ratio of 3g: 1kg.
3. Chemical control
Leaf axil filling in severely infested young plantation during April–May, September–October and December–January
using sevidol Granule @ 25 g per palm per application mixed with 200 g of sand.
breeding materials cannot be eliminated - treated with carbaryl 50 WP at 0.01 per cent on w/w basis.
4. Biological
Release of Baculovirus infected adult beetles (@ 10 – 15 beetles/ha
It is the most economical, effective and easy method for dissemination of the inoculum.
Application of M. anisopliae in the breeding sites is very effective for the control of grubs.
5. Attractants
Rhinolure vane trap hanged at a height of 10ft.
It is found to be very effective in trapping adult beetles
Castor seed powder fermented in rice water and kept in mud pots at ground level
It is an efficient method for trapping adult beetles.
Red palm weevil
Symptoms of damage
Rhinoceros beetle attacked palms are more prone to infestation by red palm weevil.
Grubs bore into stem and feed on softer tissues of stem, meristem and mesocarp of fruits.
Infested palms - gradual wilting and drying of outer whorl of fronds.
In severe - rotting of spear.
Red palm weevil lays eggs on injuries made by rhinoceros beetle on bunches.
Larvae feed on the mesocarp of fruits and penetrate into peduncle for pupation.
Infestation causes qualitative and quantitative loss of the fruits.

Identification of pest



Management
Ripe bunches are to be harvested in time. Avoid making wounds on the palm and bunches.
Prophylactic leaf axil filling is to be done for young palms as in the case of rhinoceros beetle.
Trunk injection with carbaryl 50% WP at 1% is an effective curative treatment.
Mealy bugs
Symptoms of damage
Mealy bugs infest the spear leaves of oil palm seedlings in the nursery and main field
Yellowing of young leaves and stunted growth of palms.
It is also infests the unripe and ripe oil palm fruits
pre anthesising of male and female inflorescences.
Identification of pest
Adult - White mealy bugs.
Management
Collection and destruction of infested plant parts
Collect planting material from unaffected plantation
Spraying with dimethoate at 0.03% or methyl demeton at 0.025%.
Release coccinellid beetle, Cryptolaemus montrouzieri @ 10 / tree

Nettle caterpillar
Symptoms of damage
Nettle caterpillars - stinging spines which can cause nettle rash on contact with the skin.
Caterpillars feed on the leaves
Infestation – mostly occur in outer whorl of fronds and middle whorl of fronds.
Identification of pest
Larvae are slender and greenish in colour with yellow coloured head.
Management
Cutting and burning the badly affected and dried leaves.
Spraying with Carbaryl 50% W.P. 0.1% is recommended (younger larvae are more susceptible)

Mites
Symptoms of damage
Mites suck the sap from the leaves.
Attacked leaves - discoloured and look speckeld.
Nursery and young palms are severely disrupted.
Management
Application of dicifol 2ml/lit or wettable sulphur 2g/lit.

Common mynah
Symptoms of damage
It is found to infest oil palm fruits throughout the year.
Management
Covering the fruit bunch with suitable low cost material is the simplest and effective method
Twenty two gauge galvanized iron wire mesh (60 x 90 cm) (the size depending upon the fruit bunches) used to
cover the Fresh Fruit Bunches (FFB) atleast of 3-4 times.
At least 10 cm gap between the net and the fruit bunch.
Old palm leaves - used for covering fruit bunches to protect them from avian pest.
Leaf tips of about one meter length are cut and packed at close intervals into the leaf axils.
Near the fruit bunches and tied with rope to keep them firm and impenetrable by the bird.
Other materials like plaited coconut leaf basket, reed basket, used polythene (cement) bags etc.

Rodents, Burrowing rat
Symptoms of damage
The burrowing rats burrow down to the bole of the palms and make cavities into the hole
Feed the sweet inner cabbage portion.
No external symptoms - entire meristematic region is devoured.
Suddenly the leaves look wilted or dried and death of the palm.


Management
1. Orchard sanitation
Field sanitation
Clean cultivation
2. Mechanical barrier
At the time of planting - rodent infested areas, can be covered with 22 gauge galvanized iron (chicken) wire mesh
3. Traps
Different traps are available in the market.
Cage trap, spring death trap, death fall trap, bamboo noose trap etc.
Trap shyness may become a problem after continuous use.
Cleaning and washing the traps daily
Changing the places for keeping the traps frequently etc.
4. Chemical control
A number of rodenticides are available in the market under acute poisons and chronic poisons.
Zinc phosphide - used acute poison, but induces bait shyness in rodents.
Single dose anticoagulant - Bromadiolone (0.005%). It is available in wax cake formulations.
Multiple dose anticoagulants - Warfarin, Fumarin.
The basins should be placed in the field in the evening and removed in the morning.
Dead rats should be buried to avoid secondary poisoning.
5. Biological agents
A large number of predators used to regulate the rodent population in nature.
Predators - Snakes, vultures, mongoose, cats and dogs.
Source: https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/
